High-contrast ultrafast imaging of the heart
Résumé
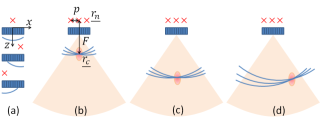
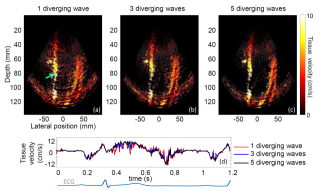
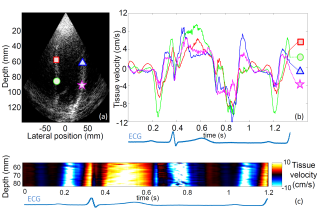
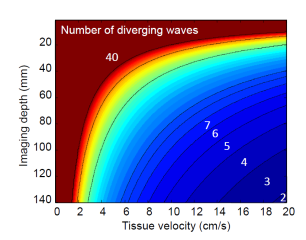
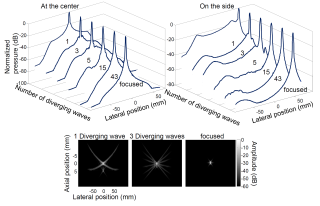
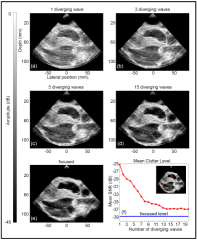
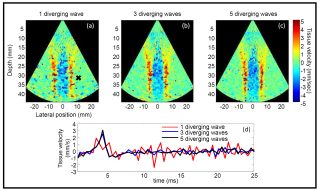
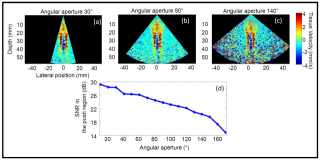
Non-invasive ultrafast imaging of intrinsic waves such as electromechanical waves or remotely induced shear waves in elastography imaging techniques for human cardiac applications remains a big challenge. In this paper we propose to perform ultrafast imaging of the heart with adapted sector size by coherently compounding diverging waves emitted from a standard transthoracic cardiac phased-array probe. As in ultrafast imaging with plane wave coherent compounding, diverging waves can be summed coherently to obtain high-quality images of the entire heart at high frame rate in a full field-of-view. To image the propagation of shear waves with a large signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), the field-of-view can be adapted by changing the angular aperture of the transmitted wave. Backscattered echoes from successive circular wave acquisitions are coherently summed at every location in the image to improve the image quality while maintaining very high frame rates. The transmitted diverging waves, angular apertures and subapertures sizes were tested in simulation and ultrafast coherent compounding was implemented in a commercial scanner. The improvement of the imaging quality was quantified in phantoms and in one human heart, in vivo. Imaging shear wave propagation at 2500 frame/s using 5 diverging waves provided a large increase of the SNR of the tissue velocity estimates while maintaining a high frame rate. Finally, ultrafast imaging with 1 to 5 diverging waves was used to image the human heart at a frame rate of 4500-900 frames/s over an entire cardiac cycle. Spatial coherent compounding provided a strong improvement of the imaging quality, even with a small number of transmitted diverging waves and a high frame rate, which allows imaging the propagation of electromechanical and shear waves with good image quality.
Fichier principal
 High_Contrast_Ultrafast_Imaging_of_the_Heart.pdf (2.06 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
High_Contrast_Ultrafast_Imaging_of_the_Heart.pdf (2.06 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_1.png (36.69 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Tissue_Velocity_for_different_number_of_diverging_waves.wmv (7.4 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_1.png (36.69 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Tissue_Velocity_for_different_number_of_diverging_waves.wmv (7.4 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_10.png (1.39 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_10.png (1.39 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_11_NEW.png (790.72 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_11_NEW.png (790.72 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_12.png (117.84 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_12.png (117.84 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
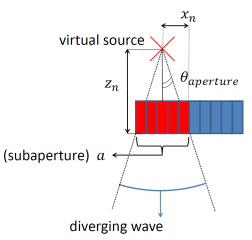 figure_2.png (48.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_2.png (48.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
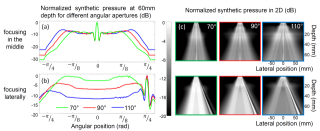 figure_3.png (955.91 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_3.png (955.91 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
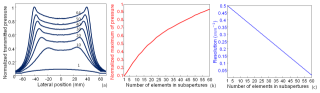 figure_4.png (74.84 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_4.png (74.84 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
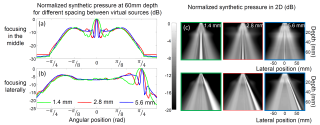 figure_5.png (874.59 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_5.png (874.59 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_6.png (394.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_6.png (394.75 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_7.png (1.26 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_7.png (1.26 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_8.png (1.75 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_8.png (1.75 Mo)
Télécharger le fichier
 figure_9.png (910.31 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
figure_9.png (910.31 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Origine : Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s)
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Vidéo
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image
Format : Figure, Image